1、手机开机后,Android系统首先会创建一个Zygote(核心进程)。
SystemServer 中有一个 main()方法为系统服务的入口;frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 public static void main (String[] args) { new SystemServer ().run(); }
在SystemServer 中的 main()方法中,就一句代码生成 SystemServer 对象,执行run 方法。在run()方法里启动了各类服务;frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 private void run () { try { traceBeginAndSlog("StartServices" ); startBootstrapServices(); startCoreServices(); startOtherServices(); SystemServerInitThreadPool.shutdown(); } catch (Throwable ex) { Slog.e("System" , "******************************************" ); Slog.e("System" , "************ Failure starting system services" , ex); throw ex; } finally { traceEnd(); } } private void startOtherServices () { t.traceBegin("StartSystemUI" ); try { startSystemUi(context, windowManagerF); } catch (Throwable e) { reportWtf("starting System UI" , e); } t.traceEnd(); } private static void startSystemUi (Context context, WindowManagerService windowManager) { PackageManagerInternal pm = LocalServices.getService(PackageManagerInternal.class); Intent intent = new Intent (); intent.setComponent(pm.getSystemUiServiceComponent()); intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_DEBUG_TRIAGED_MISSING); context.startServiceAsUser(intent, UserHandle.SYSTEM); windowManager.onSystemUiStarted(); }
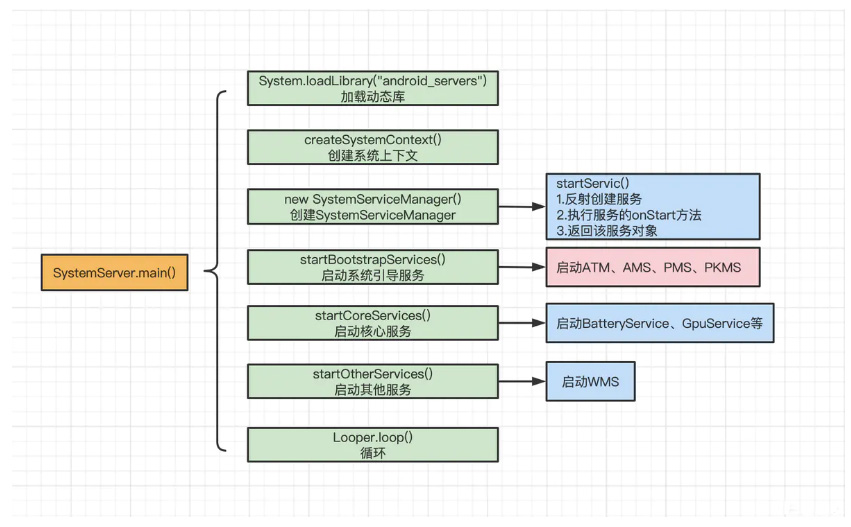
SystemServer执行流程图:
SystemUi进入到SystemUIService的onCreate()方法里;在onCreate()方法中获得 SystemUIApplication 对象并调用其 startServicesIfNeeded() 方法frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/SystemUIService.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 @Override public void onCreate () { super .onCreate(); ((SystemUIApplication) getApplication()).startServicesIfNeeded(); } public void startServicesIfNeeded () { String[] names = getResources().getStringArray(R.array.config_systemUIServiceComponents); startServicesIfNeeded(names); }
在SystemUIApplication中查看startServicesIfNeeded() 方法,其中其中 config_systemUIServiceComponents 值在frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/res/values/config.xml 里:frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/SystemUIApplication.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 private void startServicesIfNeeded (String[] services) { if (mServicesStarted) { return ; } mServices = new SystemUI [services.length]; if (!mBootCompleted) { if ("1" .equals(SystemProperties.get("sys.boot_completed" ))) { mBootCompleted = true ; if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "BOOT_COMPLETED was already sent" ); } } Log.v(TAG, "Starting SystemUI services for user " + Process.myUserHandle().getIdentifier() + "." ); TimingsTraceLog log = new TimingsTraceLog ("SystemUIBootTiming" , Trace.TRACE_TAG_APP); log.traceBegin("StartServices" ); final int N = services.length; for (int i = 0 ; i < N; i++) { String clsName = services[i]; if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "loading: " + clsName); log.traceBegin("StartServices" + clsName); long ti = System.currentTimeMillis(); Class cls; try { cls = Class.forName(clsName); mServices[i] = (SystemUI) cls.newInstance(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex){ throw new RuntimeException (ex); } catch (IllegalAccessException ex) { throw new RuntimeException (ex); } catch (InstantiationException ex) { throw new RuntimeException (ex); } mServices[i].mContext = this ; mServices[i].mComponents = mComponents; if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "running: " + mServices[i]); mServices[i].start(); log.traceEnd(); } }
可以看到 startServicesIfNeeded() 循环 start 了config_systemUIServiceComponents 里的 Service,这些服务不是四大组件之一的 Service, 而是继承自 SystemUI 接口的服务,我们称之为 SystemUI服务。
本文链接: http://longzhiye.top/2023/11/18/2023-11-18/