前言
本文主要分析 onTouch() 与 onTouchEvent() 事件的差异
正文
先看布局文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.longzhiye.intercepttouch.MyFrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:background="#000000"
android:text="Hello World!"
/>
</com.longzhiye.intercepttouch.MyFrameLayout>
|
MyFrameLayout 是一个自定义View:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| public class MyFrameLayout extends FrameLayout {
public MyFrameLayout(@NonNull Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyFrameLayout(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public MyFrameLayout(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
System.out.println("----onInterceptTouchEvent---ACTION_DOWN");
return true;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_UP:
System.out.println("----onInterceptTouchEvent---ACTION_POINTER_UP");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_DOWN:
System.out.println("----onInterceptTouchEvent---ACTION_POINTER_DOWN");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
System.out.println("----onInterceptTouchEvent---ACTION_MOVE");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL:
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
System.out.println("----onInterceptTouchEvent---ACTION_UP");
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected value: " + event.getActionMasked());
}
return false;
}
}
|
MainActivity:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
TextView textView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
textView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv);
textView.setOnTouchListener(new View.OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View view, MotionEvent motionEvent) {
switch (motionEvent.getActionMasked()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
System.out.println("----onTouch---ACTION_DOWN");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_UP:
System.out.println("----onTouch---ACTION_POINTER_UP");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_DOWN:
System.out.println("----onTouch---ACTION_POINTER_DOWN");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
System.out.println("----onTouch---ACTION_MOVE");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL:
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
System.out.println("----onTouch---ACTION_UP");
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected value: " + motionEvent.getActionMasked());
}
return true;
}
});
}
}
|
好了,开始进行分析:
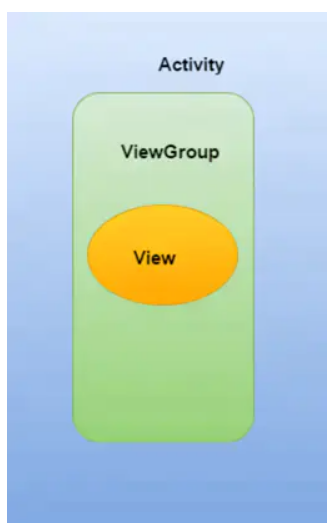
当 onInterceptTouchEvent 事件返回 true,ViewGroup会将该事件进行拦截,无法向下(View)传递。在 onTouch 中将收不到事件。
当 onTouch 事件返回 true,则表明事件不再向下传递,自己处理,消耗掉,例子:该view的 onClick 事件将会失效。
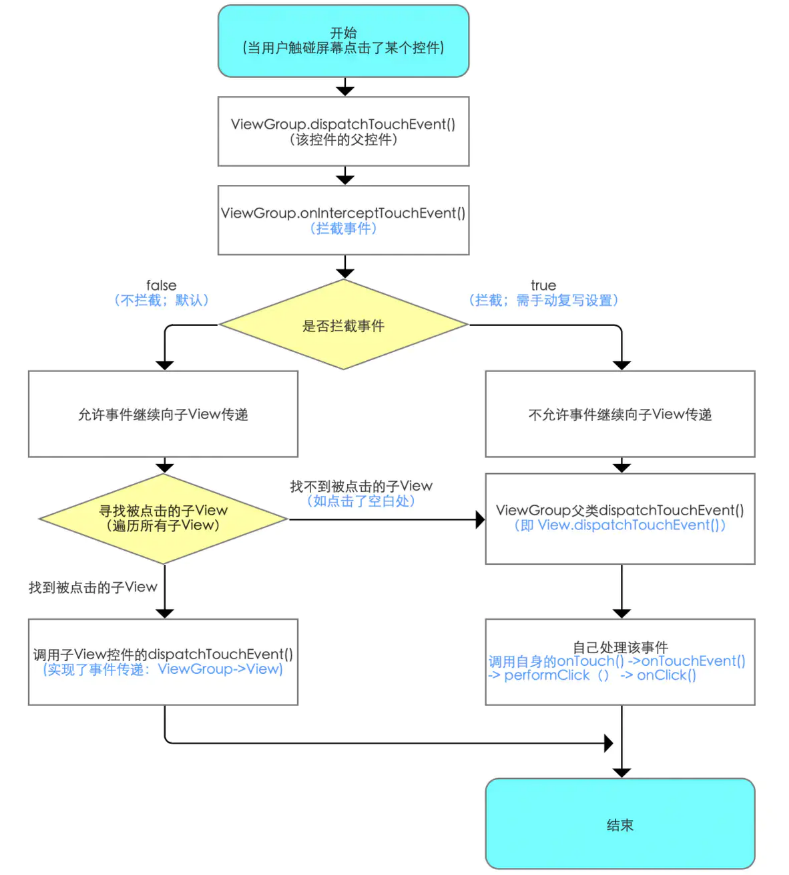
ViewGroup事件传递总结
View事件传递总结
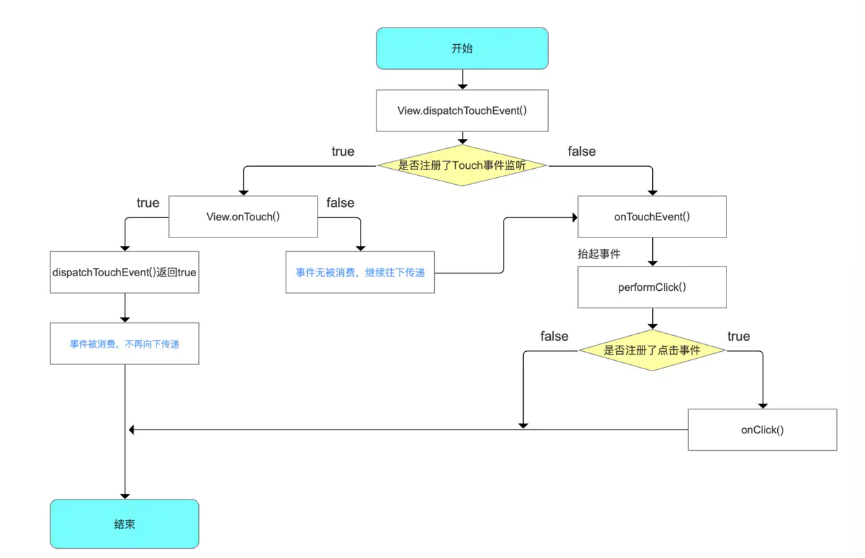
这里需要特别注意的是,onTouch()的执行 先于onClick()。
本文链接:
http://longzhiye.top/2023/12/24/2023-12-24/



