
前言
当bootloader启动后,启动kernel,kernel启动完后,在用户空间启动init进程,再通过init进程,来读取init.rc中的相关配置,从而来启动其他相关进程以及其他操作。
init进程启动主要分为两个阶段:
第一个阶段负责:
- 创建文件系统目录并挂载相关的文件系统
- 初始化日志输出
- 启用SELinux安全策略
- 为第二阶段做准备
第二阶段负责:
- 创建进程会话密钥、并初始化属性系统
- 执行SELinux第二阶段、并恢复一些文件安全上下文
- 新建epoll、并初始化子进程终止信号处理函数
- 设置其他系统属性、并开启属性服务
- 解析init.rc等文件,建立rc文件的action、service,启动其他进程
init进程如何被启动?
init进程是在Kernel启动后,启动的第一个用户空间进程,PID为1
kernel-5.10/init/main.c
1 | static int __ref kernel_init(void *unused) |
在/kernel/init/mian.c#kernel_init()方法调用了run_init_process()进行启动init进程
init进程入口
在Android Q(10.0)之前的init入口函数是init.cpp,从Android Q(10.0)开始init的入口函数是main.cpp,把各个阶段的操作分离开来,是代码更加简洁。
进入到main.cpp#main()
system/core/init/main.cpp
1 | /* |
ueventd_main()
Android根文件系统的镜像中不存在“/dev”目录,该目录是init进程启动后动态创建的。所以,建立Android中设备节点文件需要init进程完成,为此init进程创建子进程ueventd,并将创建设备节点文件的工作托付给ueventd。
ueventd通过两种方式创建设备节点文件:
第一种方式对应“冷插拔”(Cold Plug),即以预先定义的设备信息为基础,当ueventd启动后,同一创建设备节点文件。这一类设备节点文件也被称为静态节点文件。
第二种方式对应“热插拔”(Hot Plug),即在系统运行中,当有设备插入USB端口时,ueventd就会接收到这一事件,为插入的设备动态创建设备节点文件。这一类设备节点文件也被称为动态节点文件。
进入ueventd.cpp#ueventd_main()
system/core/init/ueventd.cpp
1 | int ueventd_main(int argc, char** argv) { |
init进程启动第一阶段first_stage_init.cpp
主要负责:
- 创建文件系统目录并挂载相关的文件系统
- 初始化日志输出
- 启用SELinux安全策略
- 为第二阶段做准备
system/core/init/first_stage_init.cpp
1 | int FirstStageMain(int argc, char** argv) { |
加载SELinux规则
SELinux是「Security-Enhanced Linux」的简称,是美国国家安全局「NSA=The National Security Agency」
和SCC(Secure Computing Corporation)开发的 Linux的一个扩张强制访问控制安全模块。在这种访问控制体系的限制下,进程只能访问那些在他的任务中所需要文件。
SElinux有两种工作模式:
- permissive,所有的操作都被允许(即没有MAC),但是如果违法权限的话,会记录日志,一般eng模式用
- enforcing,所有操作都会进行权限检查,一般user和user-debug模式用
不管是security_setenforce还是security_getenforce都是去操作/sys/fs/selinux/enforce文件,0表示permissive 1表示enforcing
SetupSelinux:初始化selinux,加载SElinux规则,配置SWLinux相关log输出,并启动第二阶段
system/core/init/selinux.cpp
1 | /*此函数初始化selinux,然后执行init以在init selinux中运行*/ |
SelinuxSetEnforcement():加载SeLinux规则
system/core/init/selinux.cpp
1 | void SelinuxSetEnforcement() { |
init进程启动第二阶段
主要负责:
- 创建进程会话密钥,并初始化属性系统
- 执行SELinux第二阶段,并恢复一些文件安全上下文
- 新建epoll,并初始化子进程终止信号处理函数
- 设置其他系统属性,并开启属性服务
- 解析init.rc等文件,建立rc文件的action、service,启动其他进程
system/core/init/init.cpp
1 | int SecondStageMain(int argc, char** argv) { |
信号处理
init是一个守护进程,为了防止init的子进程成为僵尸进程(zombie process),需要init在子进程在结束时获取子进程的结束码,通过结束码将程序表中的子进程移除,防止成为僵尸进程的子进程占用程序表的空间(程序表的空间达到上限时,系统就不能再启动新的进程了,会引起严重的系统问题)。
信号处理主要工作:
- 初始化信号signal句柄
- 循环处理子进程
- 注册epoll句柄
- 处理子进程终止
注:EPOLL类似于POLL,是Linux中用来做事件触发的,跟EventBus功能差不多。linux很长的时间都在使用select来做事件触发,它是通过轮询来处理的,轮询的fd数目越多,自然耗时越多,对于大量的描述符处理,EPOLL更有优势
InstallSignalFdHandler
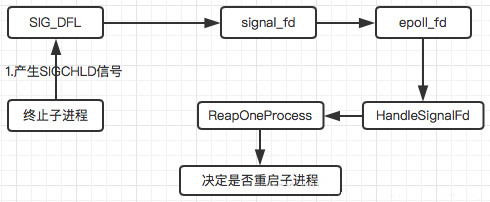
在linux当中,父进程是通过捕捉SIGCHLD信号来得知子进程运行结束的情况,SIGCHLD信号会在子进程终止的时候发出,了解这些背景后,我们来看看init进程如何处理这个信号。
- 新建一个sigaction结构体,sa_handler是信号处理函数,指向内核指定的函数指针SIG_DFL和Android 9.0及之前的版本不同,这里不再通过socket的读写句柄进行接收信号,改成了内核的信号处理函数SIG_DFL。
- sigaction(SIGCHLD, &act, nullptr) 这个是建立信号绑定关系,也就是说当监听到SIGCHLD信号时,由act这个sigaction结构体处理
- RegisterHandler 的作用就是signal_read_fd(之前的s[1])收到信号,触发handle_signal
终上所述,InstallSignalFdHandler函数的作用就是,接收到SIGCHLD信号时触发HandleSignalFd进行信号处理
信号处理示意图:

system/core/init/init.cpp
1 | static void InstallSignalFdHandler(Epoll* epoll) { |
RegisterHandler
说明:信号注册,把fd句柄加入到epoll_fd_的监听队列中
system/core/init/epoll.cpp
1 | Result<void> Epoll::RegisterHandler(int fd, Handler handler, uint32_t events) { |
HandlerSignalFd
说明:监控SIGCHLD信号,调用ReapAnyOutstadingChildren来终止出现问题的子进程
system/core/init/init.cpp
1 | static void HandleSignalFd() { |
ReapAnyOutstandingChildren
system/core/init/sigchld_handler.cpp
1 | void ReapAnyOutstandingChildren() { |
最终会调用到ReapOneProcess()方法
ReapOneProcess
说明:ReapOneProcess是最终的处理函数,这个函数先调用waitpid找出挂掉进程的pid,然后根据pid找到对应Service,最后调用Service的Reap方法清除资源,根据进程对应的类型,决定是否重启机器或重启进程
system/core/init/sigchld_handler.cpp
1 | static pid_t ReapOneProcess() { |
解析init.rc
当属性服务建立完成后,init的自身功能基本就告一段落,接下来需要来启动其他的进程。但是init进程如何其他其他进程呢?其他进程都是一个二进制文件,我们可以直接通过exec的命令方式来启动,例如 ./system/bin/init second_stage,来启动init进程的第二阶段。但是Android系统有那么多的Native进程,如果都通过传exec在代码中一个个的来执行进程,那无疑是一个灾难性的设计。
init.rc是一个配置文件,内部由Android初始化语言编写(Android Init Language)编写的脚本。类似通过读取配置文件的方式,来启动不同的进程。
LoadBootScripts
说明:如果没有特殊配置ro.boot.init_rc,则解析./init.rc
把/system/etc/init、/system_ext/etc/init、/odm/etc/init、/product/etc/init这几个路径加入init.rc之后解析的路径,在init.rc解析完成后,解析这些目录里面rc文件
注意:init.rc位于/system/core/rootdir下
system/core/init/init.cpp
1 | static void LoadBootScripts(ActionManager& action_manager, ServiceList& service_list) { |
Android7.0后,init.rc进行了拆分,每个服务都有自己的rc文件,他们基本上都被加载到/system/etc/init,/vendor/etc/init, /odm/etc/init等目录,等init.rc解析完成后,会来解析这些目录中的rc文件,用来执行相关的动作。
CreateParser
说明:创建Parser解析对象,例如service、on、import对象
1 | Parser CreateParser(ActionManager& action_manager, ServiceList& service_list) { |
执行Action动作
按顺序把相关Action加入触发器队列,按顺序为 early-init -> init -> late-init. 然后在循环中,执行所有触发器队列中Action带Command的执行函数。
1 | am.QueueEventTrigger("early-init"); |
Zygote启动
从Android 5.0的版本开始,Android支持64位的编译,因此zygote本身也支持32位和64位。通过属性ro.zygote来控制不同版本的zygote进程启动。
在init.rc的import段我们看到如下代码:
system/core/rootdir/init.rc
1 | import /system/etc/init/hw/init.${ro.zygote}.rc // 可以看出init.rc不再直接引入一个固定的文件,而是根据属性ro.zygote的内容来引入不同的文件 |
init.rc位于/system/core/rootdir下。在这个路径下还包括四个关于zygote的rc文件。
分别是init.zygote32.rc,init.zygote32_64.rc,init.zygote64.rc,init.zygote64_32.rc,由硬件决定调用哪个文件。
这里拿64位处理器为例,init.zygote64.rc的代码如下所示:
system/core/rootdir/init.zygote64.rc
1 | service zygote /system/bin/app_process64 -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server |
service zygote /system/bin/app_process64 -Xzygote /system/bin –zygote –start-system-server 解析:
service zygote :init.zygote64.rc 中定义了一个zygote服务。 init进程就是通过这个service名称来创建zygote进程
/system/bin/app_process64 -Xzygote /system/bin –zygote –start-system-server解析:
zygote这个服务,通过执行进行/system/bin/app_process64 并传入4个参数进行运行:
| 名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 参数1 | -Xzygote 该参数将作为虚拟机启动时所需的参数 |
| 参数2 | /system/bin 代表虚拟机程序所在目录 |
| 参数3 | –zygote 指明以ZygoteInit.java类中的main函数作为虚拟机执行入口 |
| 参数4 | –start-system-server 告诉Zygote进程启动systemServer进程 |
init总结
init进程主要分为两个阶段,
第一个阶段主要完成了:
- 创建文件系统目录,并挂载了相关文件系统
- 初始化了日志输出系统
- 加载了SELinux(访问控制安全模块)安全策略
- 进入第二阶段
第二阶段主要完成了
- 初始化了属性系统
- 执行了SELinux第二阶段,并恢复了一些文件的安全上下文
- 新建了epoll,并初始化了子进程终止信号处理函数
- 设置了系统其他属性,并开启了属性系统
- 解析init.rc来启动其他进程
本文链接:
http://longzhiye.top/2024/02/25/2024-02-25/